InstaGas Policy Rules Overview
InstaGas provides customizable rules for gas policies. These rules are organized into four categories:
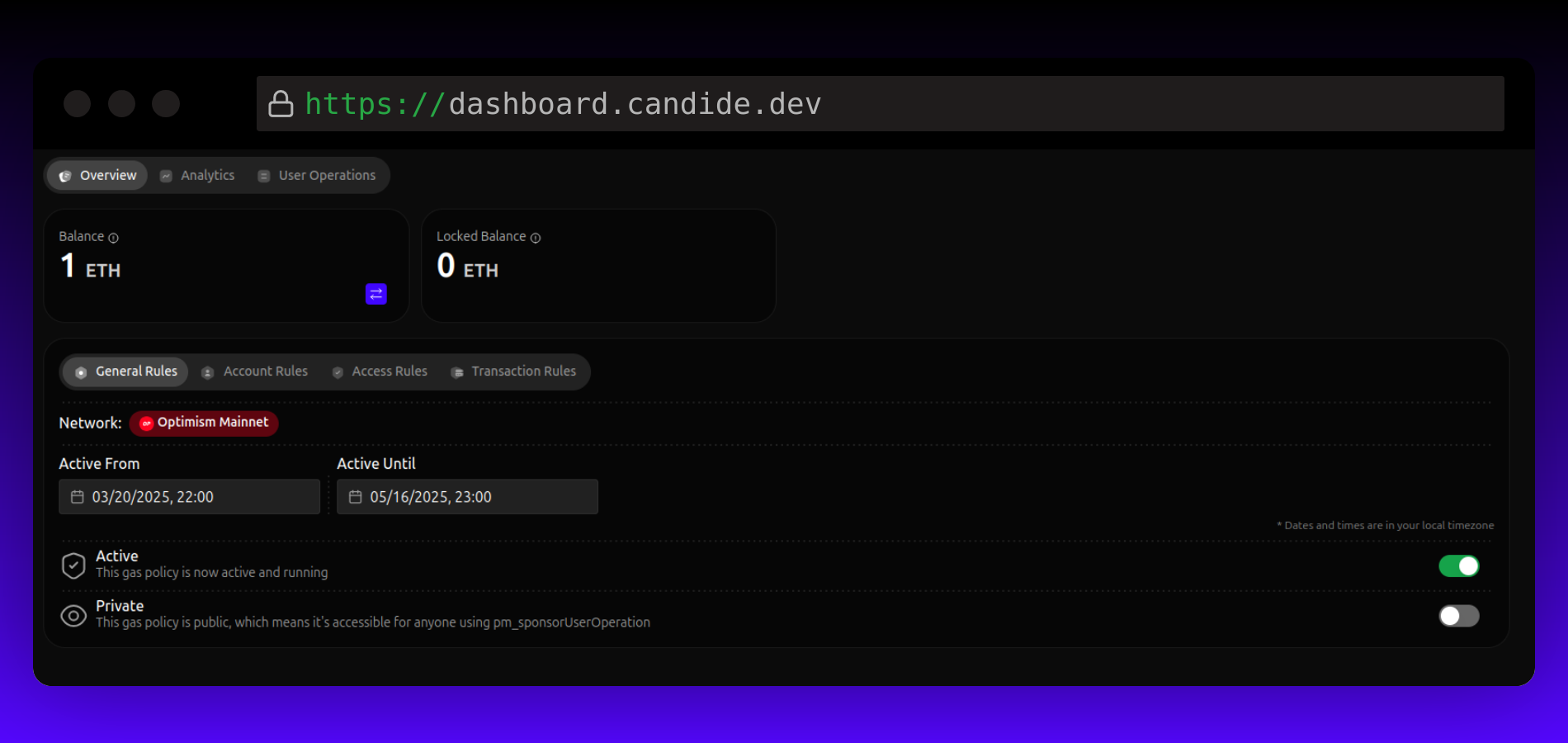
General Rules
- Effective Date Range: Specify when the gas policy should be active. This setting is ignored if the policy is inactive.
- Active State: Toggle to activate or deactivate the policy at any time.
- Private or Public: Choose between public and private gas policies:
- Public Gas Policies: Set up by dApps for wallet consumption without requiring a sponsorship policy ID.
- Private Gas Policies: Set up by wallets, requiring a sponsorship policy ID. Used when no public gas policy matches.
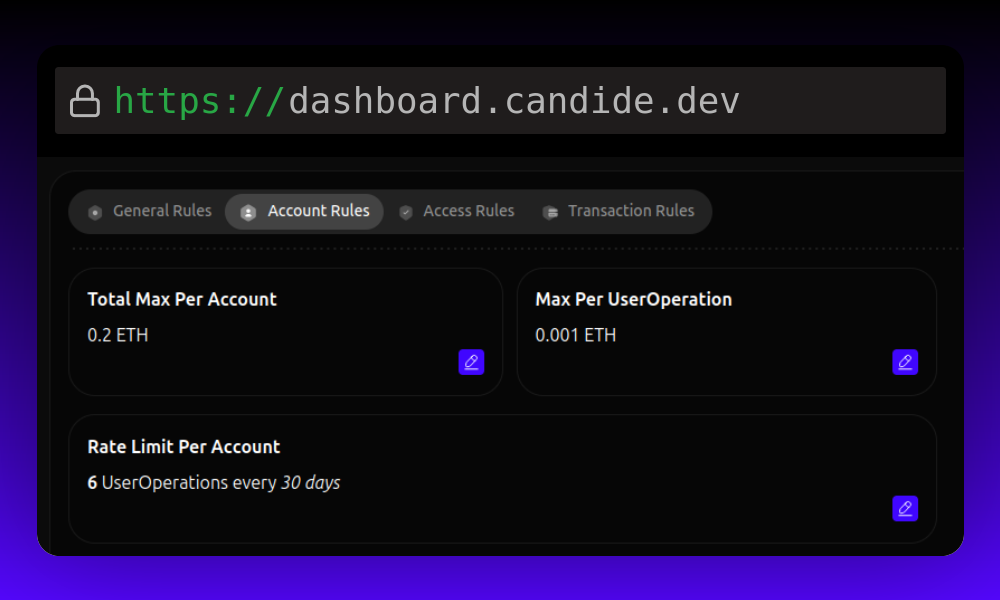
Account Rules
- Total Max per Account: Set an account spending limit.
- Example: "Each account has a total sponsorship gas limit of 0.5 ETH."
- Max per UserOperation: Limit transaction sponsorship.
- Example: "Each UserOperation can be sponsored up to 0.0001 ETH."
- Rate Limit Per Account: Define rate and period constraints.
- Example: "Each account is allowed x sponsorships per y days."
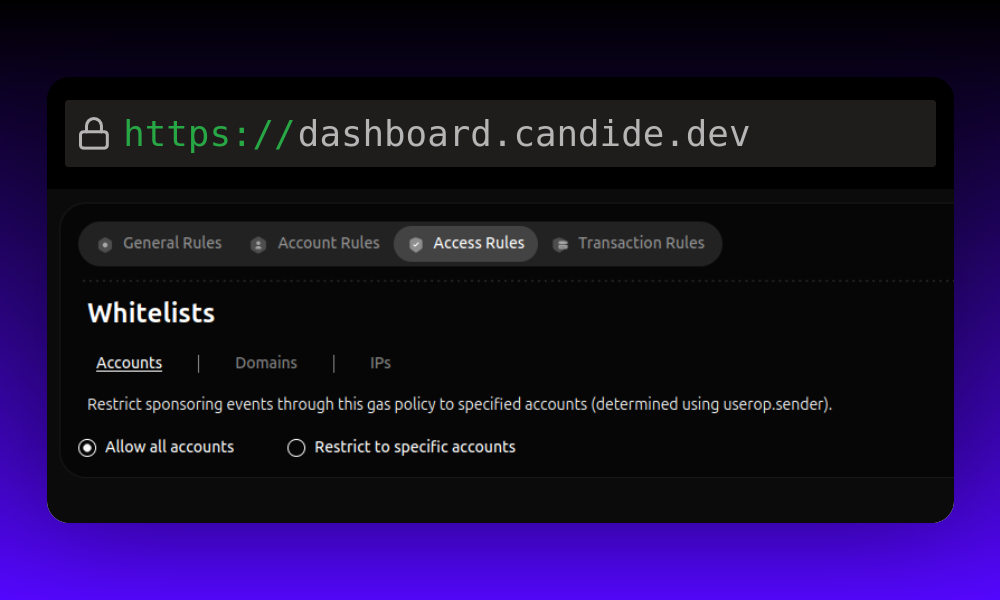
Access Rules
- Account Whitelist: Create an allowlist of accounts eligible for the gas policy. If empty, all accounts are allowed.
- Example: "Only sponsor transactions from sender
0xabcd...."
- Example: "Only sponsor transactions from sender
- Domains Whitelist: Create an allowlist of origins eligible for the gas policy. If empty, all origins are allowed.
- Example: "Only sponsor transactions originating from
app.uniswap.com."
- Example: "Only sponsor transactions originating from
- IP Whitelists: Create an allowlist of IPs eligible for the gas policy. If empty, all IPs are allowed.
- Example: "Only sponsor transactions originating from IP
148.156.123.63."
- Example: "Only sponsor transactions originating from IP
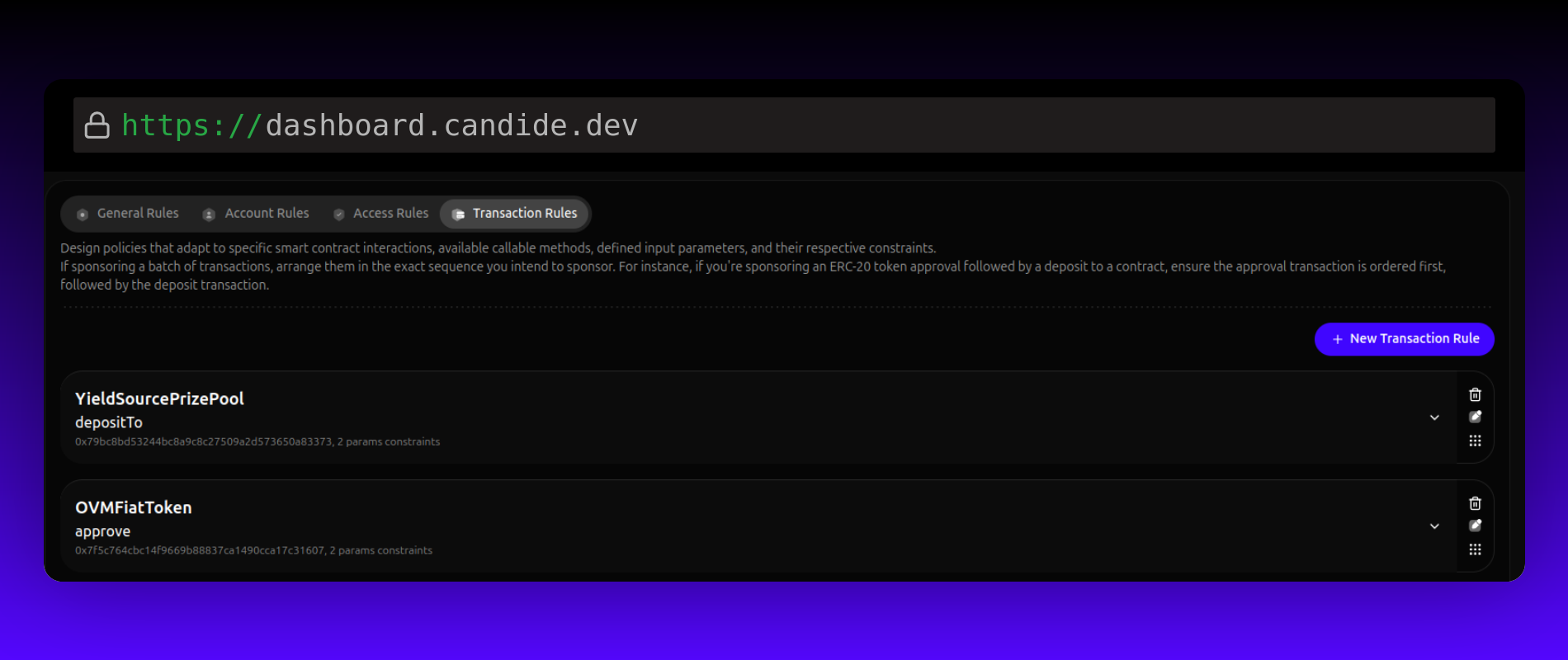
Transaction Rules
Transaction rules limit gas sponsorship to specific smart contract interactions, callable methods, input parameters, and constraints.
- Contract Address: Limit gas sponsorship to a specific smart contract address.
- Example: "Only sponsor transactions interacting with smart contract
0x123."
- Example: "Only sponsor transactions interacting with smart contract
- Method: Limit gas sponsorship to a specific callable method on the smart contract.
- Example: "Only sponsor when the transaction calls the
swapmethod."
- Example: "Only sponsor when the transaction calls the
- Parameters Constraints: Limit gas sponsorship based on method parameters and constraints.
- Example: "Only sponsor when
tokenInamount is greater than or equal to 1 ETH."
- Example: "Only sponsor when
- Batch Transaction: Design rules to sponsor transaction batches, such as an ERC-20 token approval followed by a contract deposit.
- Example: "Only sponsor if the transaction includes both ERC-20 token
approvalanddepositcalls."
- Example: "Only sponsor if the transaction includes both ERC-20 token
Example: Uniswap Swap Transaction
When you want to make a swap on Uniswap, you can make a call to the swap function with specific parameters. For instance:
swap(400, usdt, weth)
In this example:
swapis the function being called, which initiates the swap transaction.(400, usdt, weth)are the parameters being passed to theswapfunction, which specify the details of the swap:400is the amount of tokens to be swapped.usdtis the token being swapped (in this case, USDT).wethis the token being swapped for (in this case, WETH).
For each function, you can specify a list of parameters, and each parameter can have a constraint. For example, you can assign constraints to the parameters in the swap function as follows:
amount: greater than 350 (e.g.,amount > 350)tokenIn: equal to USDT (e.g.,tokenIn == usdt)tokenOut: equal to WETH (e.g.,tokenOut == weth)
By specifying these constraints, you can control the behavior of the swap transaction and ensure that it is executed according to your requirements. For instance, you can ensure that the swap transaction only occurs if the amount being swapped is greater than 350, and if the tokens being swapped are USDT and WETH.